rm Command Examples
The rm command allows you to delete both files and folders. Here's how to use it.

Creating and removing files is one of the most basic yet crucial tasks in computing and when you start embracing the terminal, the first thing you search for is "How to remove files in a Linux terminal".
The answer is you use the rm command to remove files in the Linux command line.
So in this tutorial, I will walk you through how to use the rm command with practical examples.
How to use the rm command in Linux
To use the rm command in the most effective manner, you are recommended to start with its syntax so here's a syntax for the rm command:
rm [options] <File(s)>Here,
[options]: it is used to change the default behavior of the rm command as per your linking such as using the-rflag will remove files recursively.<File(s)>: here's where you specify one or more files to remove.
You get multiple options with the rm command and here's a list of the commonly used ones:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-r or -R |
Recursively remove directories and their contents. |
-f |
Forcefully remove files without a confirmation prompt. |
-i |
Interactively prompt before removing each file. |
-v |
Verbose mode; displays detailed information about actions. |
--preserve-root |
Avoid removing the root directory ('/') and its contents. |
--no-preserve-root |
Allow removing root directory ('/') and its contents. |
--help |
Display summary of options for rm command. |
For more details, you can always check the man page of rm command.
Now, let's take a look at some practical examples of the rm command.
1. Remove a file
To remove a file using the rm command, all you have to do is append the name or path to the file to the rm command as shown here:
rm <File or path to file>For example, if I want to delete the sample.txt file, then I will be using the following:
rm sample.txt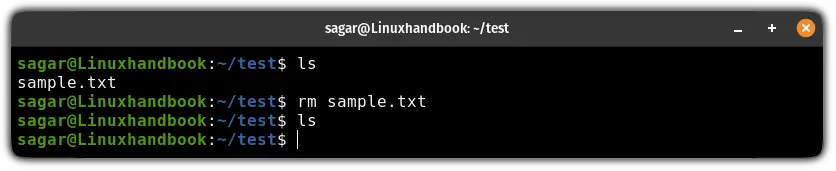
2. Remove multiple files
If you want to remove multiple files using the rm command, then all you have to do is append the target filenames to the rm command as shown here:
rm file1 file2 fileN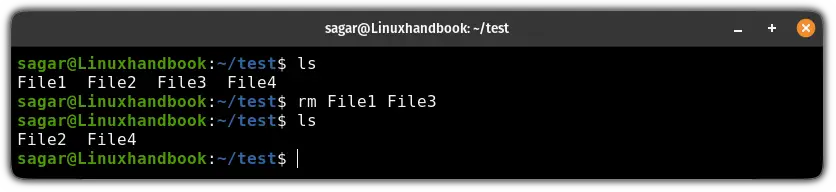
Similarly, you can use a wildcard to remove all the files having a similar file type. For example, if you want to remove all the text files at once then you can use the following:
rm *.txt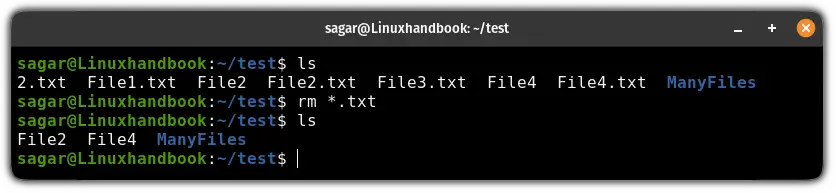
3. Remove an empty directory
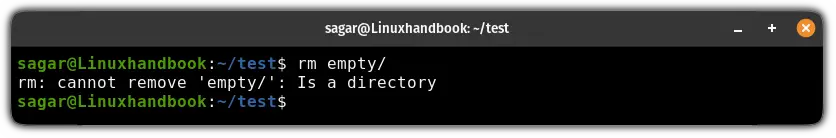
When you try to remove an empty directory with the rm command, it will throw an error message saying "rm: cannot remove: Is a directory":
To remove an empty directory, you'll have to pair the rm command with the -d flag:
rm -d <Directory or path to directory>Here's how I removed the empty directory:
rm -d empty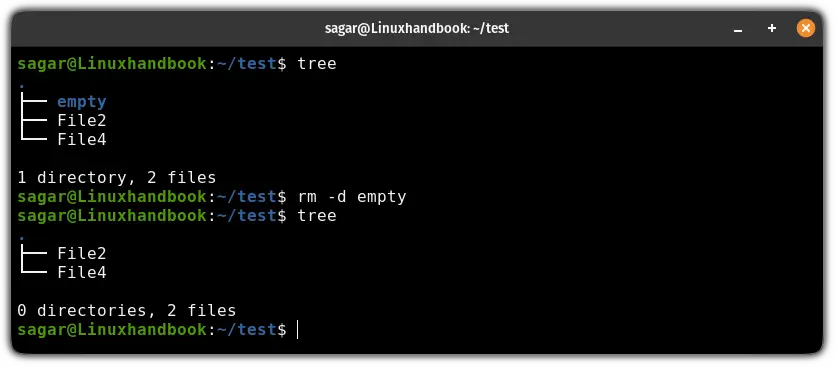
4. Remove a directory with files inside
When you try to remove a directory with the -d flag, it will throw an error saying "rm: cannot remove directory: Directory not empty":
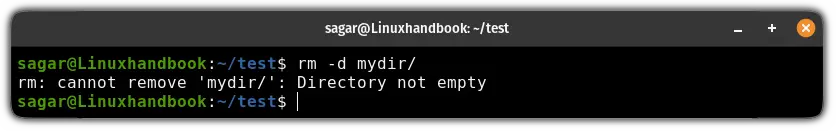
So if you want to remove a directory containing files, then you have to use the -r flag. It will instruct the rm command to remove files recursively resulting in the removal of the directory:
rm -r <Directory or path to directory>Here's how I removed the mydir directory (a non-empty directory):
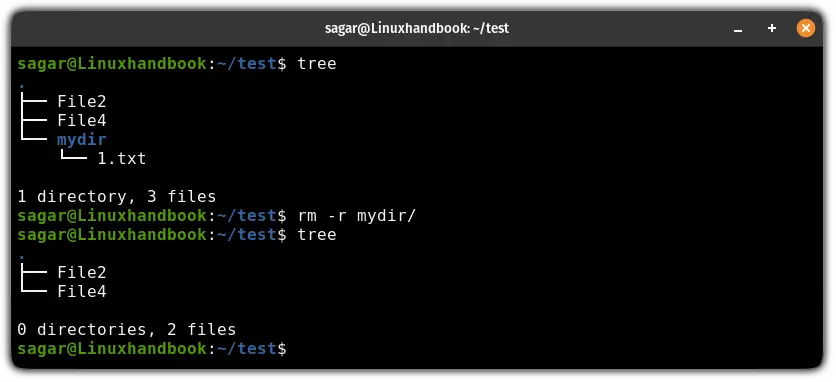
5. Remove files interactively
While removing multiple files, there are times when you remove the important files accidentally. To tackle this problem, you can interact with the rm command and choose which ones to keep and which ones to remove.
To remove files interactively, you'd have to use the -i flag as shown:
rm -i <Target>The best use of this option is when you use a wildcard to remove multiple files at once. For example, here I used the -I flag while removing all the text files at once:
rm -i *.txt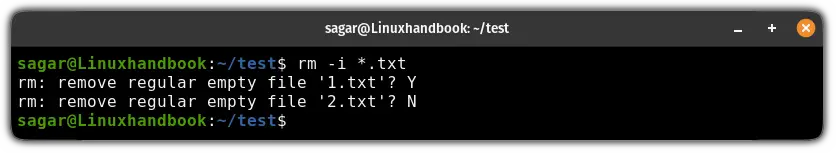
6. Remove files forcefully
When you try removing a write-protected file, it will show you a prompt if you want to remove a write-protected file or not:
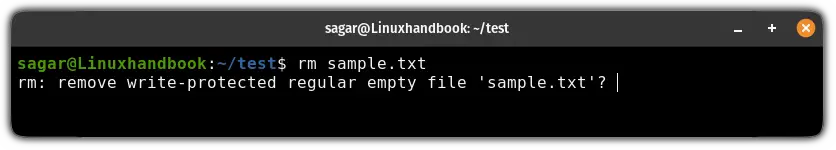
Sure, you can get away by entering Y to remove and N to not remove the file but if you are removing files recursively, then it can be a tedious task.
To solve this issue, you can use the -f flag to force remove files and it will remove files even if they are write-protected:
rm -f <File(s)>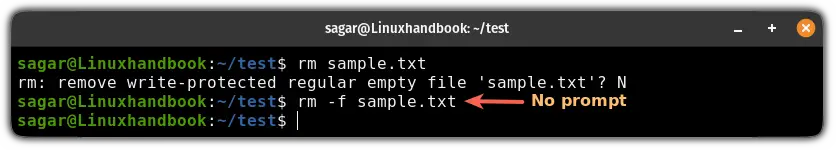
Want to remove directories only? Use rmdir instead
If you only want to remove directories, then you can use the rmdir command for convenience.
For this purpose, we wrote a detailed guide on how to use the rmdir command in Linux:

I hope you will find this guide helpful.
A software engineer who loves to tinker with hardware till it gets crashed. While reviving my crashed system, you can find me reading literature, manga, or watering my plants.

