YAML has gained a lot of popularity over the last few years as it became part of crucial DevOps tools, technologies and processes such as Ansible, Kubernetes, CI/CD pipelines and so on.
We have already covered lots of tutorials on Ansible and Kubernetes. I thought of covering YAML essentials so that you must be aware for a smoother working with your DevOps tools configuration.
What is YAML?
YAML stands for "YAML Ain't Markup Language" originally was an acronym for 'Yet Another Markup Language'. YAML is a “data serialization” language and basically a human-readable structured data format.
It is designed to be read and write friendly. The object serialization feature of YAML presents itself as a practicable alternative to JSON. YAML is a superset of JSON with the use of indentation-based scoping to denote the structure like Python.
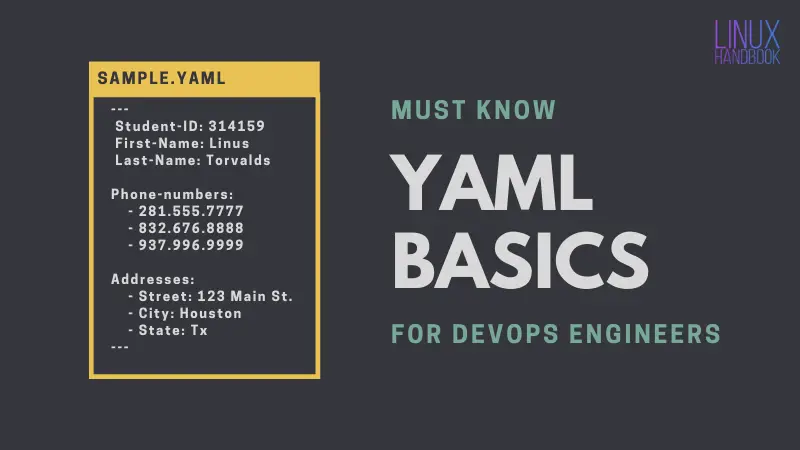
Here's a sample YAML example:
---
Student-ID: 314159
First-Name: Linus
Last-Name: Torvalds
Phone-numbers:
- 281.555.7777
- 832.676.8888
- 937.996.9999
Addresses:
- Street: 123 Main St.
- City: Houston
- State: Tx
---YAML basic rules you should always remember
If you don't want to see repeated errors while parsing your YAML file, you must always keep the following in your mind while working on YAML:
- Tabs are NOT allowed in YAML. You should use space for indention.
- Though the amount of space doesn't matter as long as the child node indentation is more than the parent, it is a good practice to keep the same number of spaces.
- There must be space between different elements of YAML (explained later).
- YAML is case-sensitive.
- YAML file should end with extensions like
.yamlor.yml. - YAML allows UTF-8, UTF-16 and UTF-32 encoding.
Let's understand the YAML syntax now.
Elements of a YAML file: Basic syntax
A YAML file is used to describe data. In a YAML file the content is all about a collection of key-value pairs where the value can be anything ranging from a string to a tree.
Let us understand it by an example. This is a Kubernetes service manifest file.
kind: Service
metadata:
name: web-app-svc
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 8080 #service port
targetPort: 8080 #Pod Port
nodePort: 30012 #Node Port from the range - 30000-32767
selector:
app: web-appIt's self explainable that it's a set of key value pair elements: Name: Value.
As you can see from the file above, a YAML file is constructed of a number of different elements. Together, they can be used to describe a wide variety of structures.
1. Spaces or indentation
In YAML, you indent with whitespace, not tabs. And there MUST be a space between elements.
Correct specification:
Kind: ServiceIncorrect specification:
Kind:ServiceBecause there is no space after the colon in the above statement!
2. Comments in YAML
Comments in YAML can be defined by placing a hash in front of an item '#'. Comments can be made at the start of a line of anywhere in the line.
Here's an example.
#Configuring the port
ports:
- port: 8080 #service port
targetPort: 8080 #Pod Port
nodePort: 30012 #Node Port from the range - 30000-32767 As you can see, it has one single line comment and three inline comments.

3. Scalar (key-value)
Scalars are the strings and numbers that make up the data on the page. In simple terms they are the key value pairs.
kind: Service
metadata:
name: web-app-svc4. Collections & Lists
List and collection elements or members are the lines that begin at the same indentation level, starting with a dash followed by a space.
- web-app-prod
- prod-deployments
- prom-monitoredIt is a basic list with each item in the list placed in its own line with an opening dash.
5. Nested collections
If you want to create a nested sequence with items and sub-items, you can do so by placing a single space before each dash in the sub-items.
-
- web-app-prod
- prod-deployments
- prom-monitored
-
- web-app-test
- staging-deployments
- not-monitored6. Dictionaries
Dictionaries comprise a key: value format with contents indented.
ports:
- port: 8080 #service port
targetPort: 8080 #Pod Port
nodePort: 30012 #Node Port from the range - 30000-32767You can merge and mix-up collections of lists and dictionaries like this:
ports:
- port: 8080 #service port
targetPort: 8080 #Pod Port
nodePort:
- 30012
- 30013
- 30014These are very basic concepts of YAML but essential for a DevOps engineer.
You don't need special editor for YAML. Your favorite text editor should already be supporting YAML or use a plugin if required.
There are many things you can dig deeper and learn. For that, you may always refer to YAML's official documentation.
And if you want, we have an online t0ol to quickly check your YAML files for any syntax errors.

Want to be a better sysadmin or DevOps? Do become a Linux Handbook member today.