
Nmap is an open source utility for network discovery and security auditing. You can use it for penetration testing, network analyzing and more.
It is a utility with vast options but the goal of this tutorial is to show you various ways of scanning ports.
scanme.nmap.org website as our target for scanning.Basic scan for open ports
With the -sT parameter, nmap can do a simple TCP scan to look for open ports:
nmap -sT scanme.nmap.org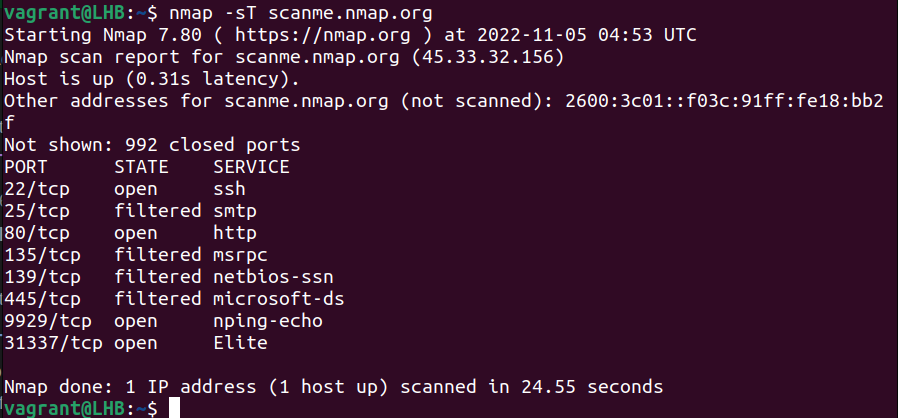
You can see that there are two important open ports on the target – 22 and 80.
These ports are used by SSH and HTTP services respectively. If these ports were not active earlier, you should check the system logs of the target system for a possible security breach.
In case you are looking for a UDP port scan for servers that run on UDP ports, use:
sudo nmap -sU scanme.nmap.org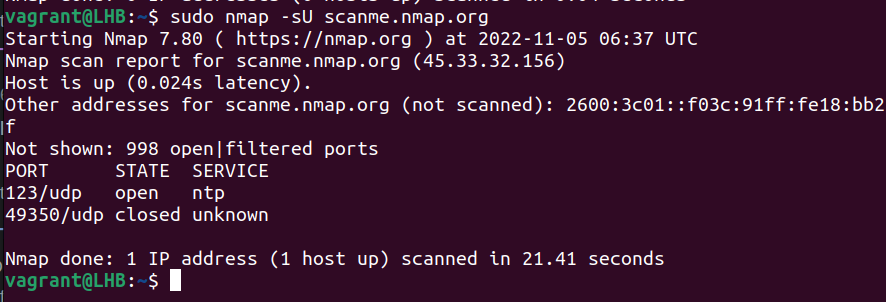
Also, it is important to note that, unlike TCP, for scanning UDP ports, you need to have root privileges.
Scanning a specific port
At its most basic, Nmap can scan a single port by just specifying the target port number with the -p option.
Let’s see some popular port scan examples:
Apache Port 80 and 443: Port 80 is the default port number for HTTP requests on Apache. You can scan it with Nmap as:
nmap -p 80 scanme.nmap.orgSimilarly, for https traffic on port 443 (the default port number), you can use the Nmap scanning as:
nmap -p 443 scanme.nmap.org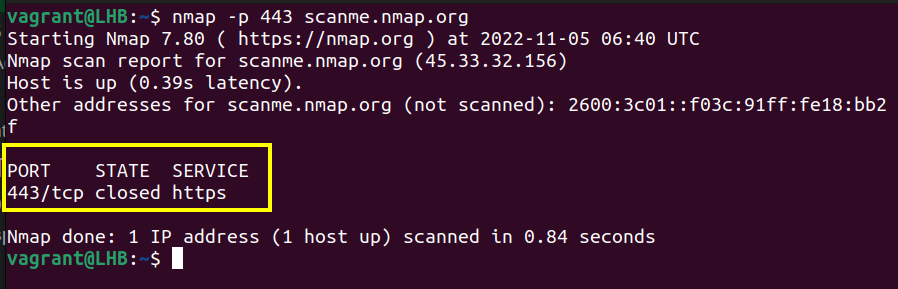
The default port number for SSH connection is 22, so in this case the Nmap scanning command will be:
nmap -p 22 scanme.nmap.orgOne thing to note here is that you can also use the name of the port instead of its number; for example, for SSH scanning, you can use:
nmap -p ssh scanme.nmap.org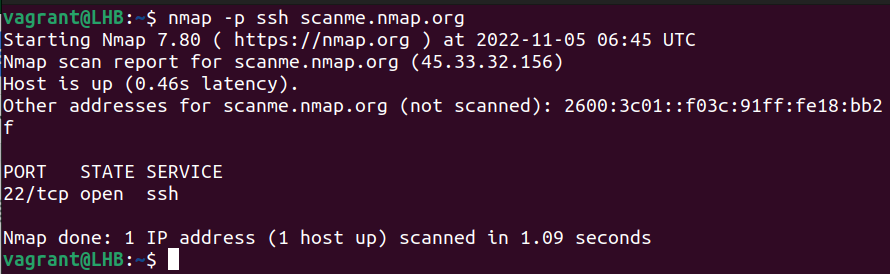
These are only two examples to show you how Nmap scanning works on a protocol with a given protocol number. You can use other protocol numbers in the same way.
A brief list of some of the commonly used ports and protocols is given below:
- 20: FTP data
- 21: FTP control port
- 22: SSH
- 23: Telnet (Insecure, not recommended for most uses)
- 25: SMTP
- 53: DNS services
- 67: DHCP server port
- 68: DHCP client port
- 80: HTTP - Unencrypted Web traffic
- 143: IMAP mail port
- 161: SNMP
- 443: HTTPS - Secure web traffic
- 587: SMTP - message submission port
Scanning multiple ports
To scan multiple ports, you need to separate them with commas as shown here:
nmap -p 22,25,80 scanme.nmap.org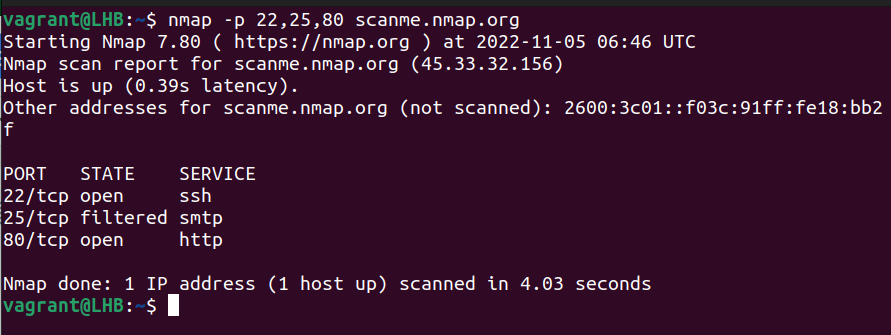
Specify multiple ranges.
nmap -p 80-85,130-140,22 scanme.nmap.org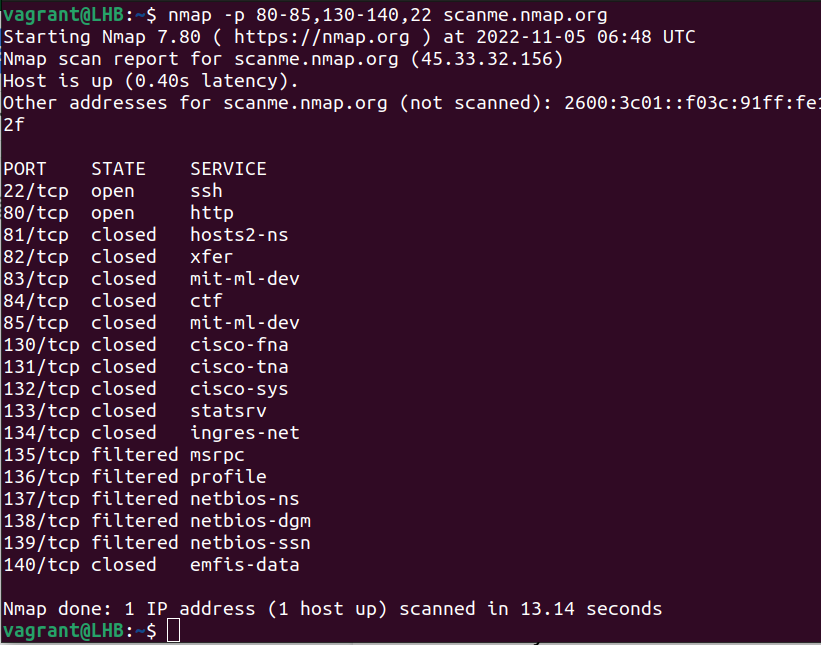
You can do further customization to port ranges. For example, you can remove the starting port to start scanning from port one:
nmap -p -22 scanme.nmap.org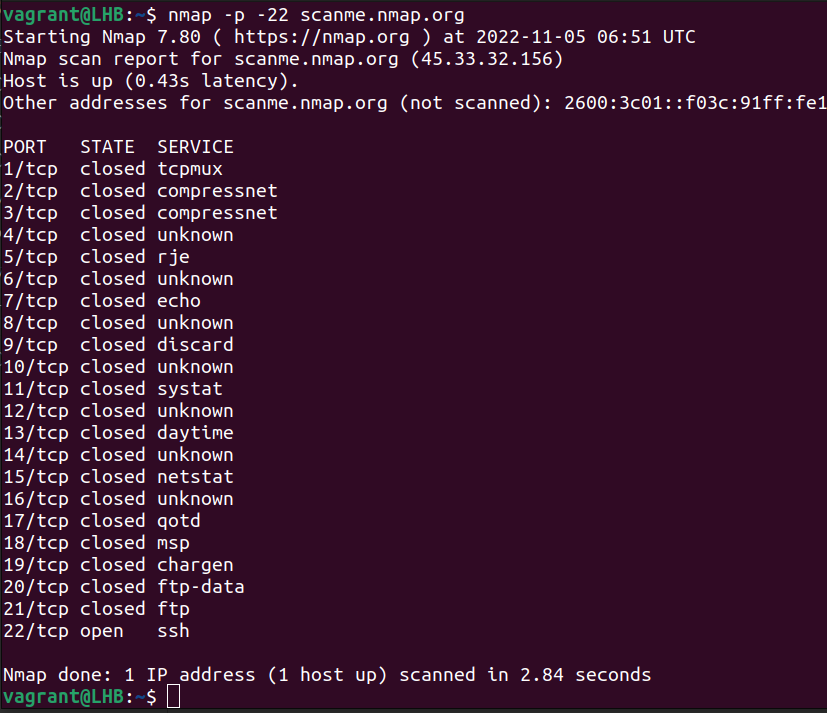
Similarly, you can exclude the last port to scan up to the last possible port:
nmap -p 65255- scanme.nmap.org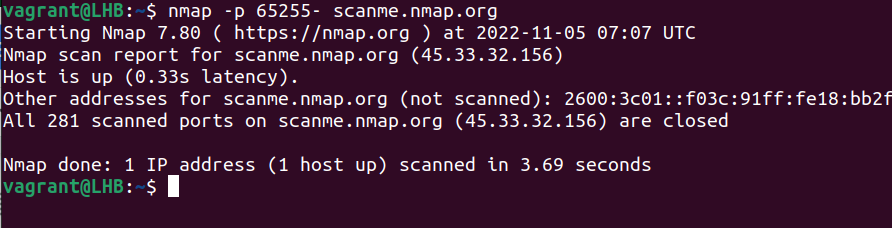
Using Wildcards with Nmap
Using wildcards can also simplify a scanning task. Suppose you want to scan all http-related ports:
nmap -p http* scanme.nmap.org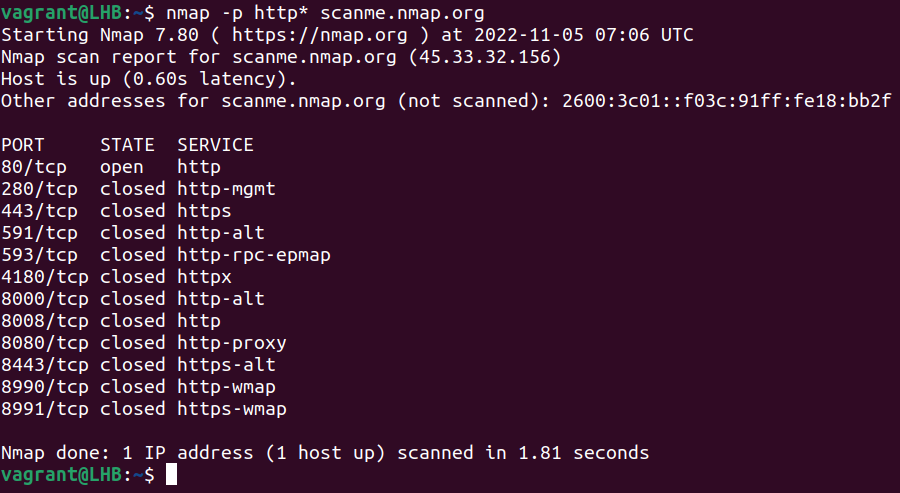
Scanning the top-ports
Scanning all the 65,536 ports of each protocol is a time-consuming task. However, most of these ports are hardly open. Nmap developer Fyodor, a big applause to him for his excellent tool, has reduced the headache of scanning this huge range of ports.
He has picked up the most prevalent TCP and UDP ports by researching millions of IP addresses and exploring many enterprise networks.
In a nutshell, based on his research, to cover 90% of the open ports, you need to target only 576 TCP ports and 11,307 UDP ports. The --top-ports option scans only the most common ports.
nmap --top-ports 1000 scanme.nmap.org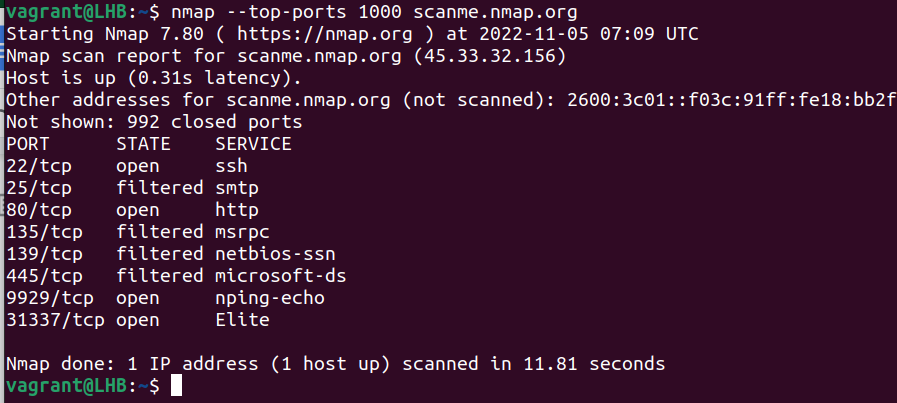
The -F option scans only the top 100 ports.
There are several ways to execute port scanning using Nmap. The most commonly used are these:
For scanning TCP connection, you can use the -sT flag:
sudo nmap -sT scanme.nmap.orgFor scanning UDP connection, you can use the -sU flag:
sudo nmap -sU scanme.nmap.orgFor scanning both the TCP and UDP open ports, you can use:
sudo nmap -n -PN -sT -sU -p- scanme.nmap.orgFor scanning SYN packets, you can use the -sS flag:
sudo nmap -sS scanme.nmap.orgConclusion
In this article, I have shown you how to use Nmap for scanning ports on a server. You can also use netstat and ps commands in parallel with Nmap to identify services using the scanned ports.

