When working with Bash scripts, you might encounter situations where you need to check if an array is empty or not.
There are two ways of knowing it:
if [[ -z "${array1[@]}" ]]; thenHere, you get all the elements of the array and use the string comparison to see if the resultant string is empty or not.
Alternatively. you can use:
if [ ${#array1[@]} -eq 0 ]; thenThis time, we got the size of the array and test it with the number zero.
Let's see both methods with sample examples.
Check empty bash array with string comparison
We are going to use two elements to check if bash array is empty or not. One is ${#array[@]} and other is the -z operator.
Here, the ${#array[@]} is used in Bash for array expansion, allowing you to access all elements of an array. Don't confuse it with ${array[*]} which treats the entire array as a single string.
The -z operator on the other is used to test whether a string is empty.
Now, let's combine both of these and write a simple bash script:
#!/bin/bash
array1=('1' '23' '4' '56' '78' '9' '0')
array2=()
if [[ -z "${array1[@]}" ]]; then
echo "array1 is empty"
else
echo "array1 is not empty"
fi
if [[ -z "${array2[@]}" ]]; then
echo "array2 is empty"
else
echo "array2 is not empty"
fiHere, I took two arrays: array1 which is filled with strings and array2 which is empty.
Later, I used the if-else twice to check each array. The first if statement will check for the array1 and the second one will verify the array2.
Once you execute the script, it will show you the following output:
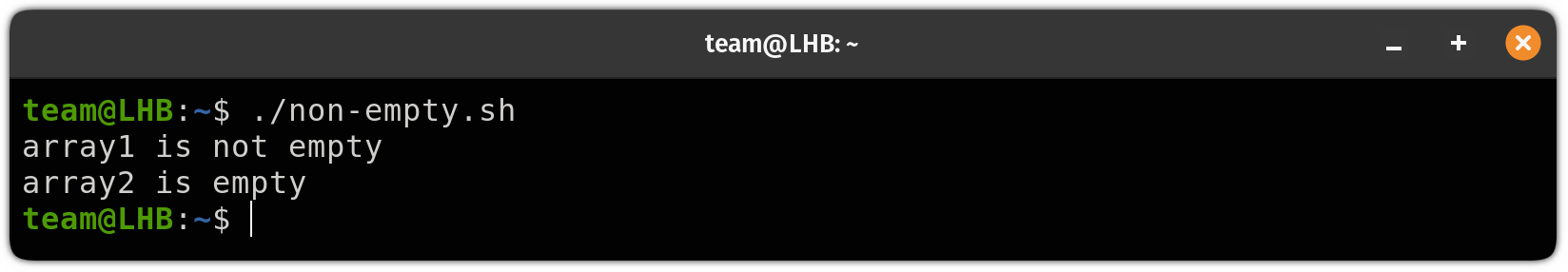
Check empty bash array with size comparison
This method checks if the array size in bash is equal to zero or not using the test operator -eq.
#!/bin/bash
array1=('1' '23' '4' '56' '78' '9' '0')
array2=()
if [ ${#array1[@]} -eq 0 ]; then
echo "array1 is empty"
else
echo "array1 is not empty"
fi
if [ ${#array2[@]} -eq 0 ]; then
echo "array2 is empty"
else
echo "array2 is not empty"
fiNotice what I did here? I simply compared the value of the array to zero and if it is true, then the array is empty and if not, then the array has some values.
Bonus: Using shortcuts with logical operators
This is the quickest way to check if the array is empty or not where you will be using the && operator with the -z operator and ${#array[@]}.
Here's the simple syntax where I have used the && operator with the echo command which will be executed if the value of -z "${array[@]}" is true:
#!/usr/bin/env bash
array=()
[[ -z "${array[@]}" ]] && echo "array is empty"That's it!
Have any doubts? Leave us a comment 😄

