
Most Linux distros use systemd as an init service which is responsible for starting, managing, and stopping services.
There are multiple reasons one would want to start the service on boot.
The major reason is you are using Linux as a web server and you want to start certain services automatically when the system boots up.
To start a systemd service on boot, all you have to do is the enable flag with the systemctl command in the following manner:
sudo systemctl enable <service-name>Want more details? I got you!
How to start a systemd service on boot
To use the systemd init service, you have to utilize the systemctl command which offers different flags for different purposes.
Let's say you create a new systemd service. You can start it immediately using the start flag. But the problem (or should I call the nature of this flag) is the effect will only remain until the next boot.
This means the service you started will be turned off while you reboot your system which is not a desirable output in most cases.
Therefore, you have a different option enable.
To use the enable option, you'd have to follow the given command syntax:
sudo systemctl enable <service_name>But some users may face the following error while using the systemctl command:
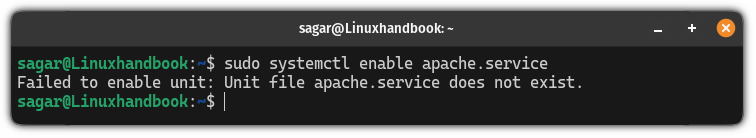
That is simply because you used the wrong name for the service and systemctl can not identify the specified service.
In that case, you can list the available services in Ubuntu using the following command:
service --status-all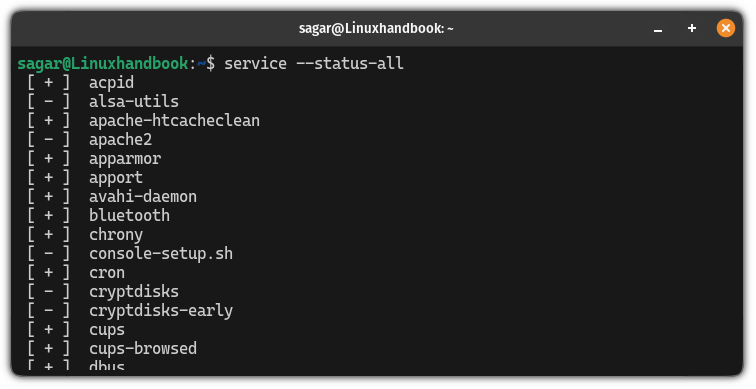
Once you find the name of the service, you can use the systemctl command again to enable the service.
For example, earlier I used apache instead of apache2 so my command to start the apache2 service would look like this:
sudo systemctl enable apache2.service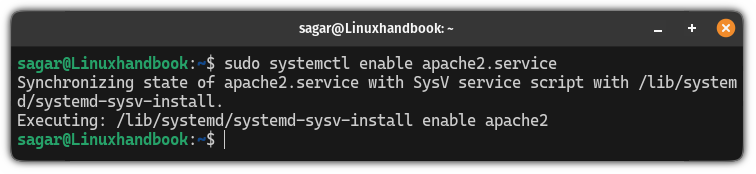
There you have it.
Create a custom systemd service
Did you know that you can create a custom systemd service? Want to know how?
Here's a detailed guide explaining how you can create custom systemd service:

I hope you will find this guide helpful.


