
Cron jobs are an excellent way of automating tasks at a predefined time in Linux. From continued backups to system resource usage, it can do many things that make the life of a Linux sysadmin easier.
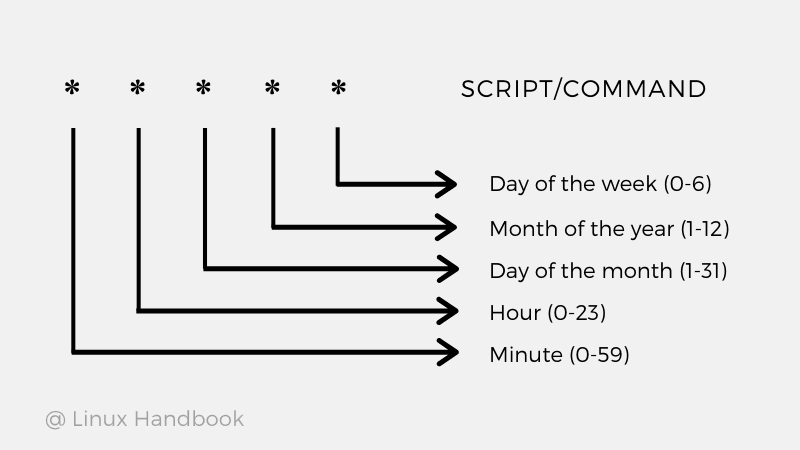
At times, you'll notice that cron jobs didn't run as expected. Checking the cron logs is the first step of troubleshooting.
Stopping, starting, or restarting the cronjobs is part of the troubleshooting process.
In this quick tutorial, I'll share how to stop, start or restart cron services in Linux.
How to start cron job
If the cron daemon is not started in the Linux system, the cron job will not execute. You have to start the cron service first.
Like most other things in Linux, the way of handling services is also different. This is why I am listing different commands for Debian and Red Hat systems.
For Redhat/CentOS:
service crond startOn older versions of Redhat and Centos, use:
/etc/init.d/crond startFor Ubuntu and Debian Systems:
sudo service cron startOn older versions, you can use the following:
sudo /etc/init.d/cron startYou won't see anything in the output if the commands run successfully. How do you know if cron job is running then? Check the status of the cron service with the following:
sudo service cron statusIt should show the active status:
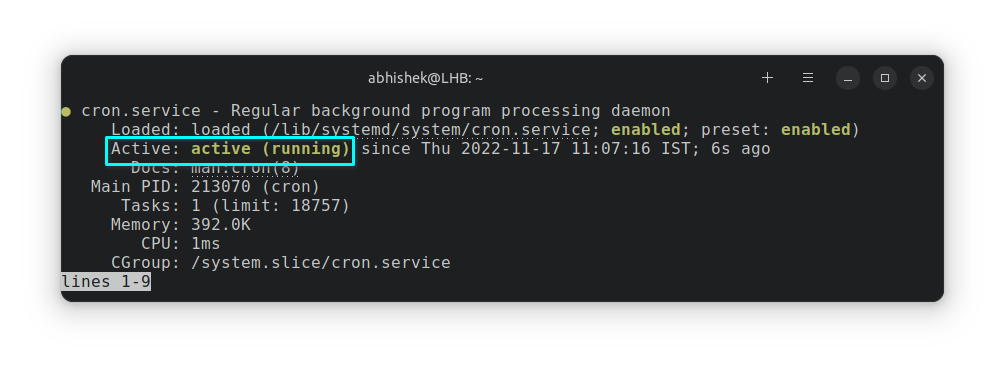
That takes care of starting cron services. Let's see about stopping it.
How to stop cron job
If you don't want to keep on running cron jobs, stop it until your troubleshooting is over. You can start it again after that.
On Redhat and CentOS, use the command below to stop the cron service:
service crond stopFor older versions, use:
/etc/init.d/crond stopFor Ubuntu and Debian, you can use this command:
sudo service cron stopor use the below command for older versions:
sudo /etc/init.d/cron stopYou can check if the cron service is stopped or not using the command:
sudo service cron statusIt should show an inactive state:
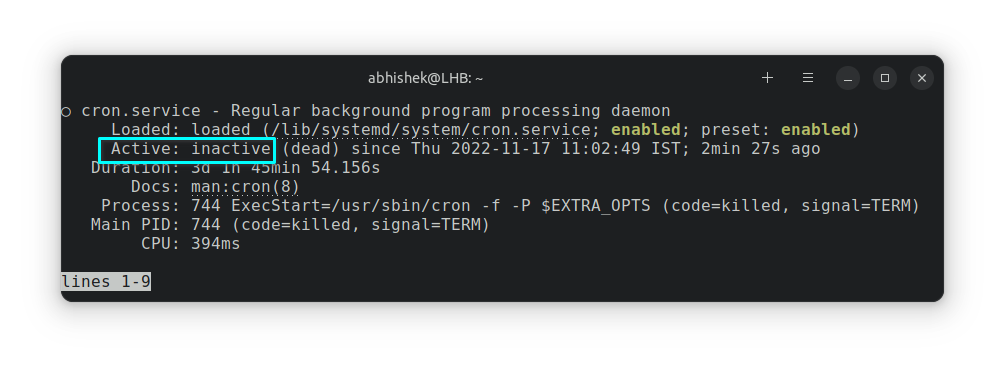
How to restart the cron job
Did you try turning it off and on again? Jokes apart, restarting often fixes things on its own. While troubleshooting, you may try restarting the cron service as well.
On Redhat and CentOS
service crond restartOr try the older commands:
/etc/init.d/crond restartFor Ubuntu and Debian systems, use
sudo service cron restartThe older command can also be tried.
sudo /etc/init.d/cron restartRestart is equivalent to stopping and starting the service again. You can try that as well.
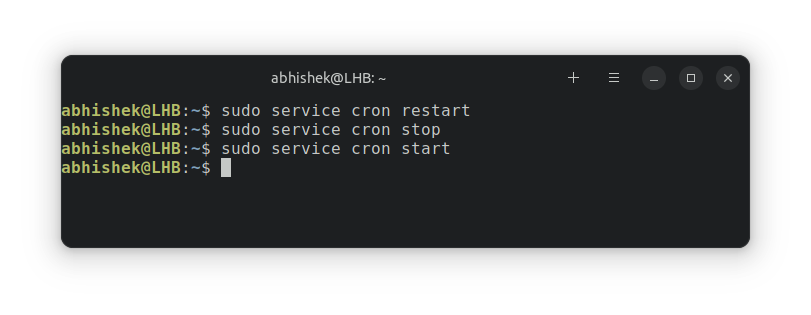
I hope you will have got a good understanding of the cron jobs and how to start, stop, and restart them.
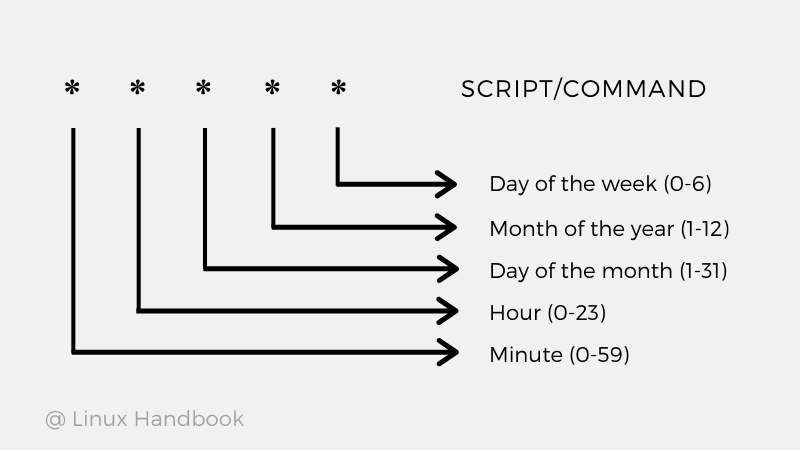
If you are new to Cron, you can refer to our beginner's guide to cron.


