In simple terms, concatenation refers to connecting two character stings.
For example, there are two character strings: snow and ball. So when you'd concatenate them, it will form a single string snowball.
While using Linux, you'd often find yourself in a situation where you have to concatenate two or more files.
So in this guide, I will share multiple examples to concatenate files.
How to concatenate files in Linux
When you consider the concatenation of text files in Linux, the cat command rules the whole category.
For demonstration, I will be using two text files named TextFile1 and TextFile2 and their file contains are as follows:
sagar@LHB:~$ cat TextFile1
File contents of TextFile1
sagar@LHB:~$ cat TextFile2
File contents of TextFile2Now, let's jump to the examples part.
Concatenate multiple files in standard output
This is the simplest concatenation that is used by most of the users where you combine the output of multiple files in the standard output:
cat TextFile1 TextFile2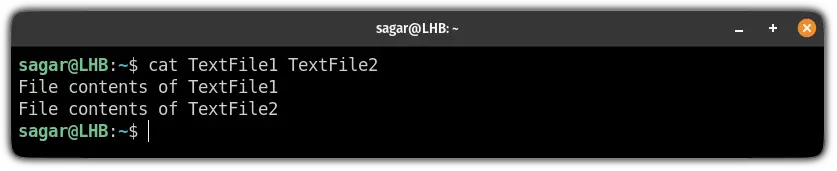
Concatenate and save file contents to a new file
Above, I explained how you can concatenate multiple files but it won't save any changes.
So if you want to concatenate files and save the output to another file, you can redirect the output data stream to a new file.
For example, here, I have concatenated the file contents of TextFile1 and TextFile2 and saved the output to a new file named Output_File:
cat TextFile1 TextFile2 > Output_File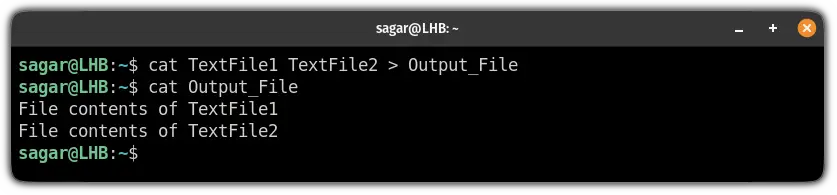
But it will override the file contents of Ouput_File (if any) and you may lose sensitive data.
To concatenate and save the output to another file without overriding, use the >> instead of >:
cat TextFile1 TextFile2 >> Output_File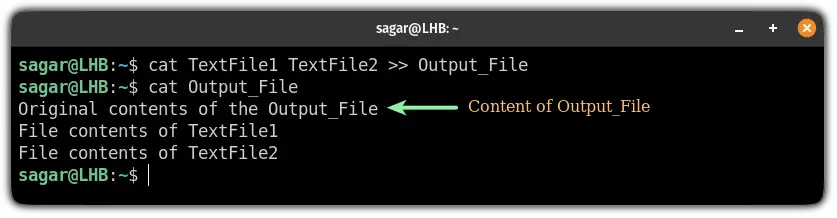
And as you can see, the contamination of two files was saved below the content of Output_File.
Add additional data from standard input while concatenation
It's not always the case where you just want to concatenate the file contents of two different files, you may also want to add additional data to it.
So let's say I want to concatenate two files TextFile1 and TextFile2 but I want to add some additional data and in that case, using the standard input is the best choice.
Which can be invoked by the - flag.
For example, I want to add data above the content of TextFile1, so I will be using the following:
cat - TextFile1 >> TextFile2It will be executed as a normal cat command where you add simple text.
Once you are done adding text, save the file and exit from using the Ctrl + D.
For your reference I added the following line:
Text from the standard output that should be placed above the file contents of TextFile1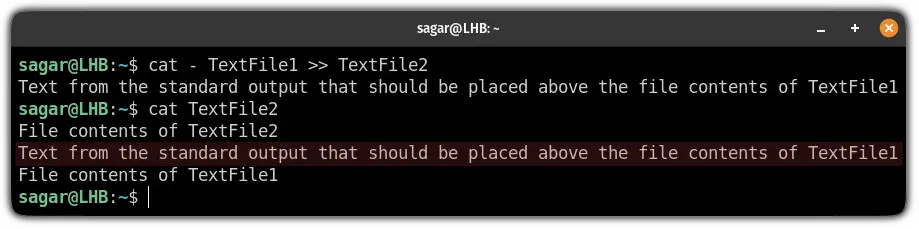
And as you can see, here, I concatenated two files with additional data from the standard input.
Similarly, if you want to add additional data after the contamination of two files instead of the above, you can refer to the following:
cat TextFile1 - >> TextFile2Here, I have entered the following in the standard input:
Content from standard input that will be placed after contents of two files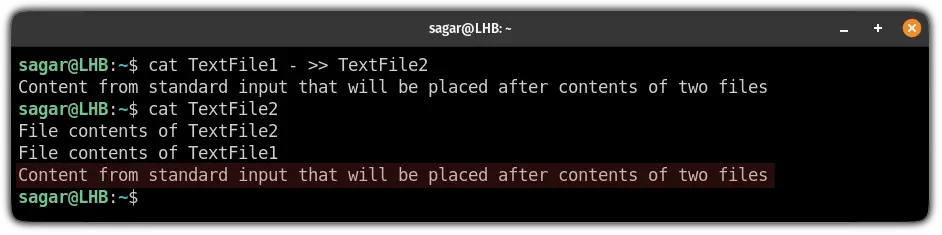
Concatenate command output to file
If you want to concatenate the output of a command to a specific file using the cat command, you can refer to the given command syntax:
Command | cat > fileFor example, here, I have concatenated the kernel version that I'm currently using to a file named Kernels:
uname -r | cat > Kernels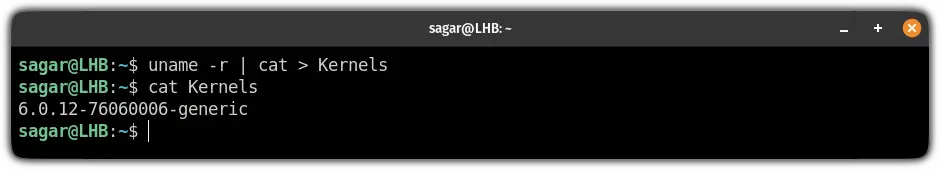
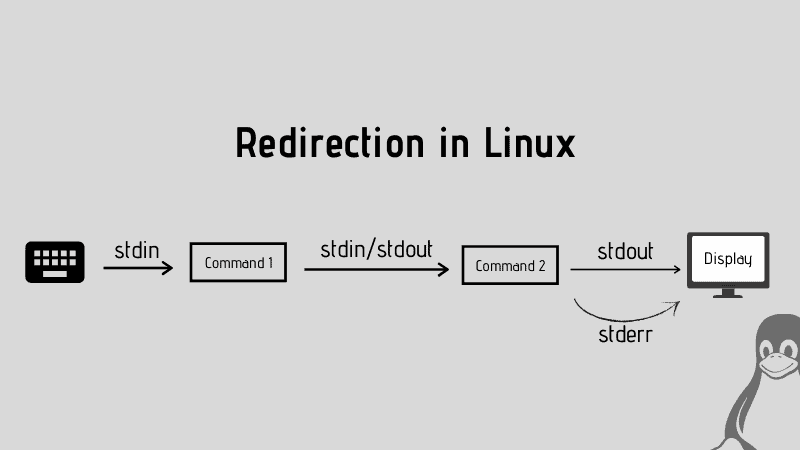
But did you know that you can also redirect the output, errors, and standard input to a file?
It is quite easy and can be very helpful in cases where you just want to concatenate the errors only:
Get more out of the cat command
While most of the users use the cat command to create and read files but what if I tell you that you can do a lot more with it?
Even I wasn't aware of its power until I read the following guide:

I hope you will find this guide helpful.
And if you have any queries, feel free to ask in the comments.